 Import CSV to Rails
Import CSV to Rails
Let’s import data from a CSV to a database table.
We don’t need a gem for that, because CSV processing is inbuilt in the Ruby language: Official Ruby CSV documentation
rails g scaffold user username email name surname phone preferences
First, create a route for the import:
# app/config/routes.rb
resources :users do
collection do
post :import
end
end
Now we can have a form that will accept only CSV files:
# app/views/users/_import.html.erb
<%= form_tag import_users_path, method: :post, multipart: true do %>
<%= file_field_tag :file, accept: ".csv" %>
<%= submit_tag '⚙️ Import' %>
<% end %>
Render the _import partial in any view:
# app/views/users/index.html.erb
<%= render "import" %>
Handle the form submission in the controller.
# app/controllers/users_controller.rb
def import
return redirect_to request.referer, notice: 'No file added' if params[:file].nil?
return redirect_to request.referer, notice: 'Only CSV files allowed' unless params[:file].content_type == 'text/csv'
CsvImportService.new.call(params[:file])
redirect_to request.referer, notice: 'Import started...'
end
There will be a lot of CSV-related logic, so it’s better to extract it into a Service:
# app/services/csv_import_service.rb
class CsvImportService
require 'csv'
def call(file)
opened_file = File.open(file)
options = { headers: true, col_sep: ';' }
CSV.foreach(opened_file, **options) do |row|
# map the CSV columns to your database columns
user_hash = {}
user_hash[:email] = row['Email Address']
user_hash[:username] = user_hash[:email].split('@').first
user_hash[:name] = row['First Name']
user_hash[:surname] = row['Last Name']
user_hash[:preferences] = row['Favorite Food']
user_hash[:phone] = row['Mobile phone number']
User.find_or_create_by!(user_hash)
# for performance, you could create a separate job to import each user
# CsvImportJob.perform_later(user_hash)
end
end
end
Result:
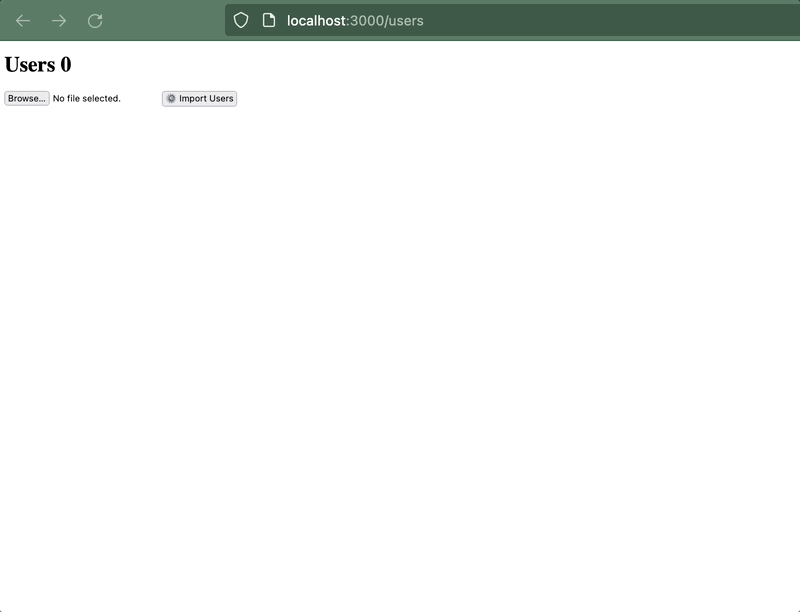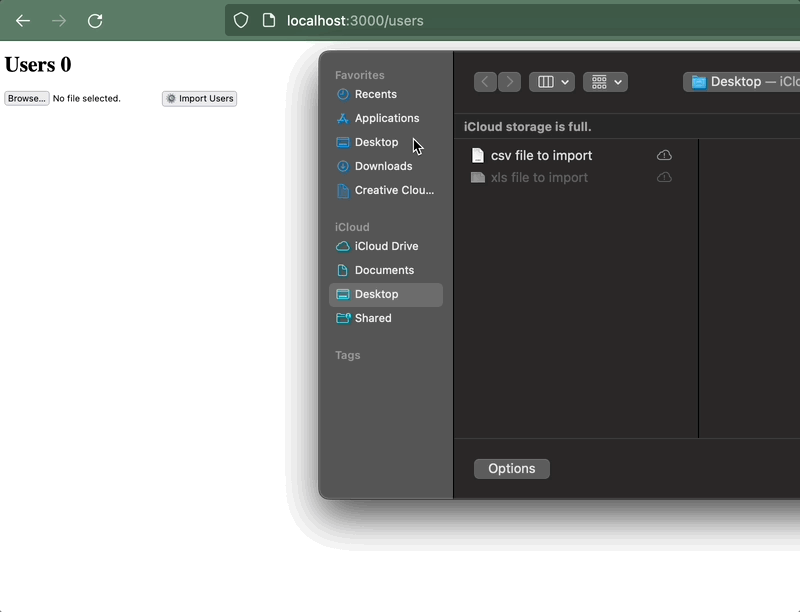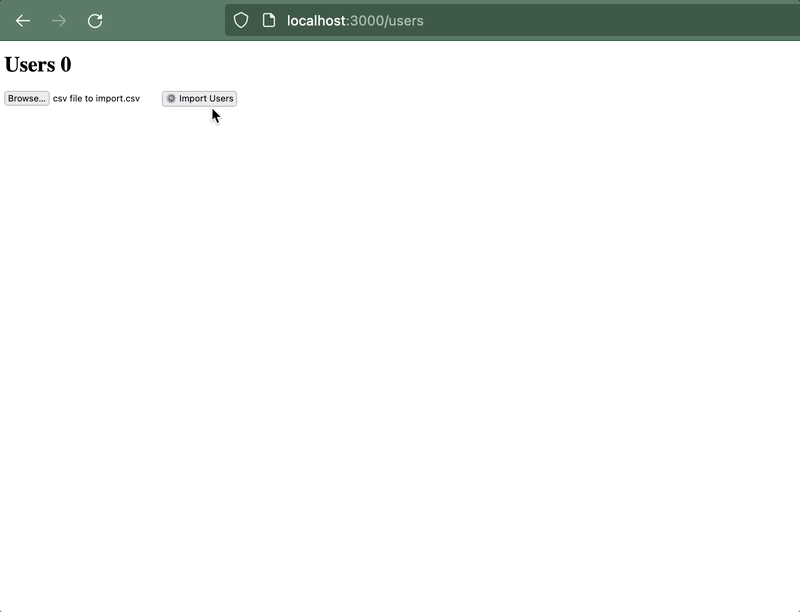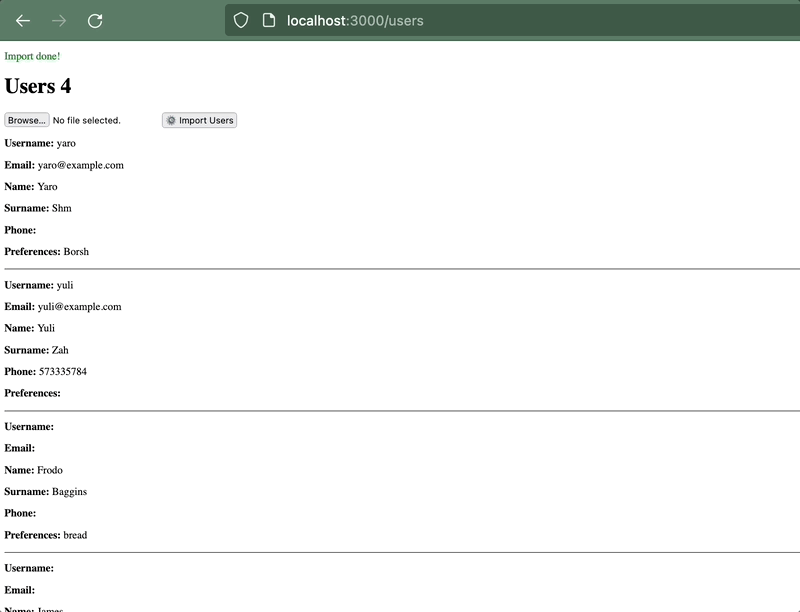
Very useful CSV commands that I discovered along the way:
# csv inside file block
File.open(file) do |file|
CSV.parse(file, headers: true, col_sep: ";")
end
# open a file
file = File.read(file) => string
file = File.open(file) => object
csv = CSV.parse(file, headers: true, col_sep: ";")
options = { headers: true, col_sep: ";" }
csv = CSV.parse(file, **options)
csv = CSV.open(file, **options)
csv = CSV.read(file.path, **options) # alternative - no need to read/open file
kv_hash_csv = csv.each.to_a.compact
kv_hash = csv.map(&:to_h)
csv.headers
# gets header values (first row)
csv.each { |row| p row }
csv.each { |row| p row.to_hash }
# manipulate a row
csv.each do |row|
row
row.to_hash
row.headers
row.fields
# option 1 (if CSV headers = User.attributes)
row_hash = row.to_hash
User.find_or_create_by!(row_hash)
# option 2
email = row['Email Address']
username = email.split('@').first
name = row['First Name']
surname = row['Last Name']
preferences = row['Favorite Food']
phone = row['Mobile phone number']
User.find_or_create_by!(email:, username:, name:, surname:, preferences:, phone:)
# option 3 (best)
user_hash = Hash.new
user_hash[:email] = row['Email Address']
user_hash[:username] = user_hash[:email].split('@').first
user_hash[:name] = row['First Name']
user_hash[:surname] = row['Last Name']
user_hash[:preferences] = row['Favorite Food']
user_hash[:phone] = row['Mobile phone number']
# user_hash[:abc] = "xyz"
User.find_or_create_by!(user_hash)
end
Alternatively to find_or_create_by you might sometimes want to use
upsert
or
upsert_all
to find existing records by a unique key and update their attributes based on the CSV.
That’s it! P.S. Kudos @secretpray
Did you like this article? Did it save you some time?