 Rails CRUD API requests with Faraday
Rails CRUD API requests with Faraday
Gems like Faraday and HTTParty enable you to make HTTP API requests to external services. The two gems are both good and very much alike, so it does not really matter which one you use.
Many API adapter gems rely on Faraday or HTTParty.
To try making and HTTP request locally from your console with Faraday, you can run a rails server in one tab, rails console in another tab, and make Faraday requests in the console. You will see http requests happening in your server logs:
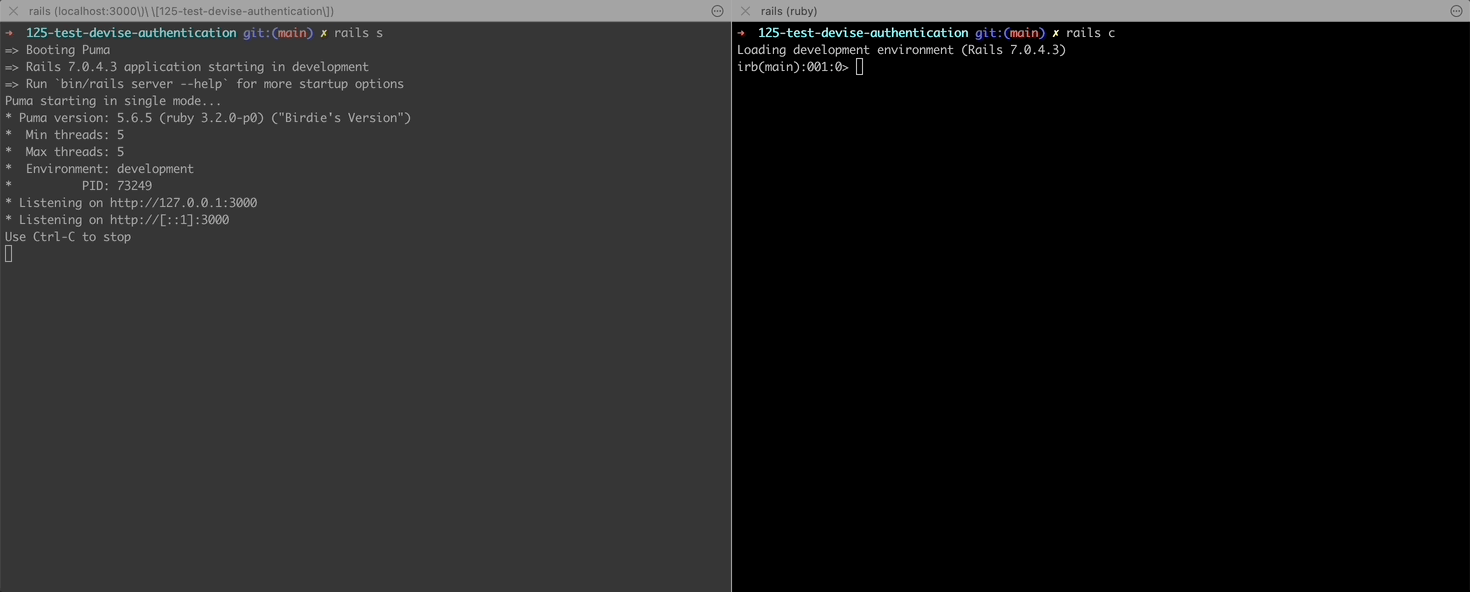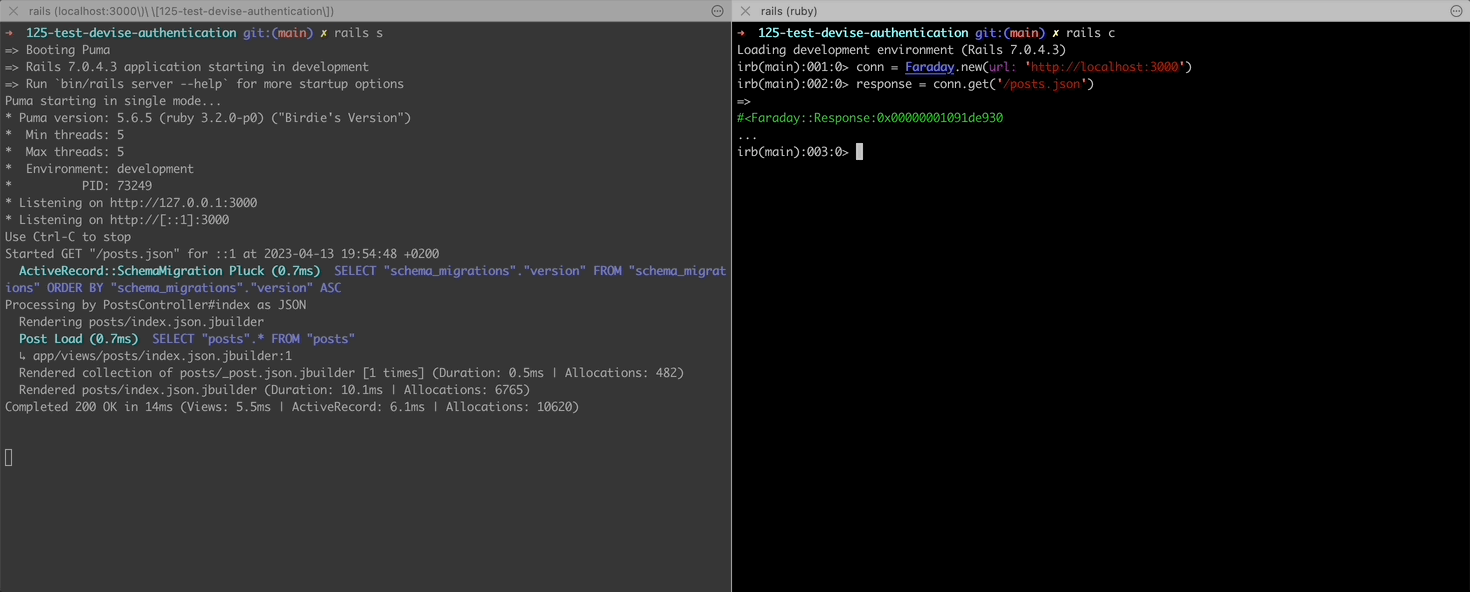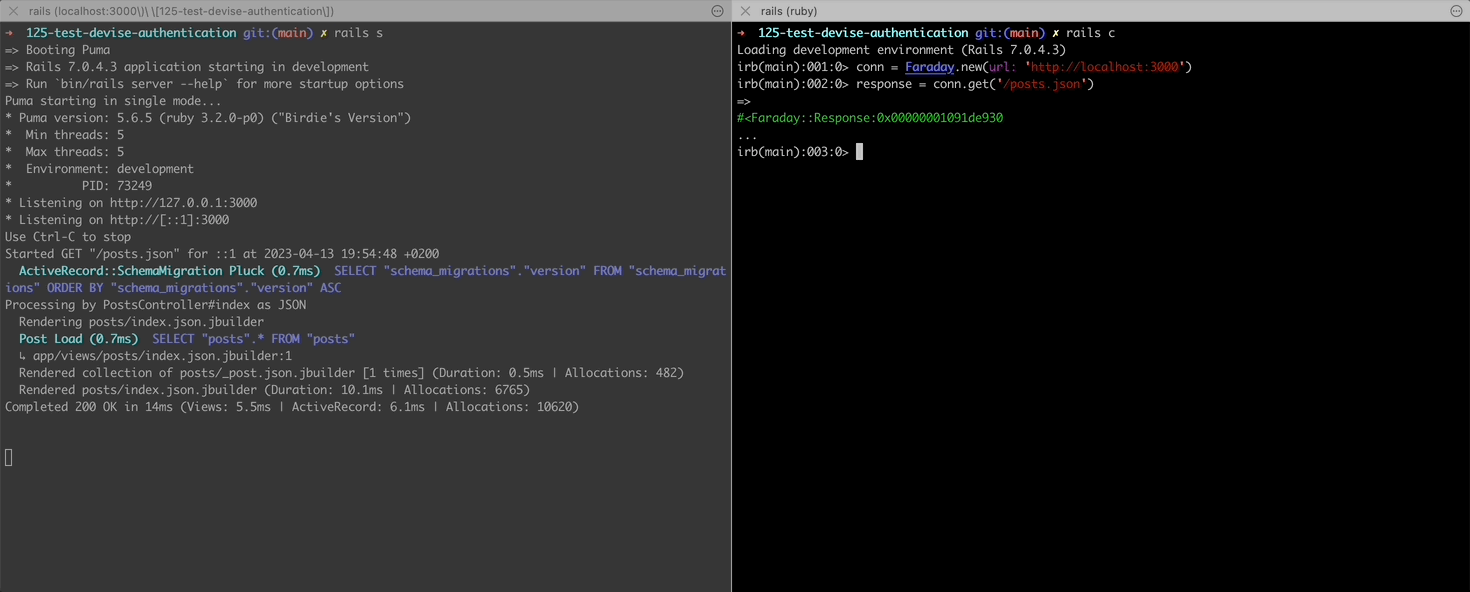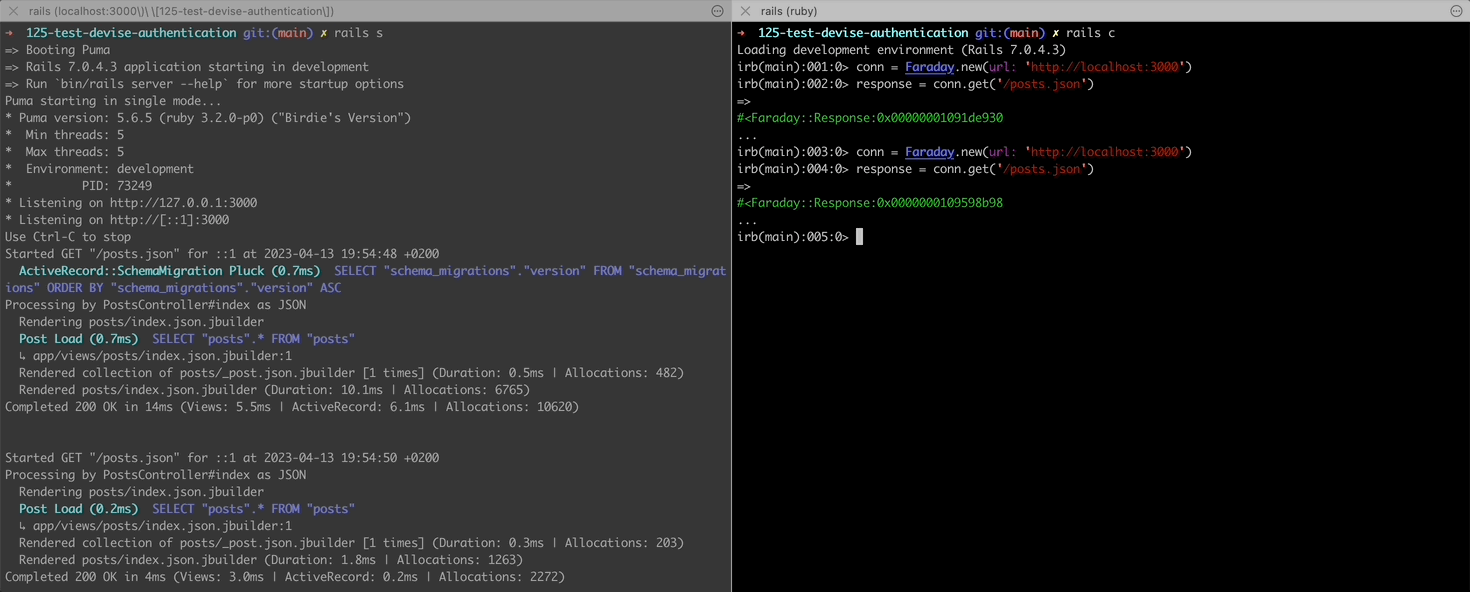
Let’s create a Post scaffold and make some CRUD requests:
bundle add faraday
rails g scaffold Post title:string body:text published:boolean published_at:datetime
rails db:migrate
Before we continue, enable non-get API requests:
# app/controllers/posts_controller.rb
protect_from_forgery with: :null_session
# skip_before_action :authenticate_user!
GET/read
Basic GET request (with optional Bearer authentication):
require 'faraday'
conn = Faraday.new(url: 'http://localhost:3000') do |faraday|
# Set the Authorization header with the Bearer token
faraday.request :authorization, 'Bearer', 'MySecretKey'
end
response = conn.get('/posts.json')
# response = conn.get('/api/v1/home/index')
response.headers
response.status
response.body
body_json = JSON.parse(response.body)
# transform a JSON object to a ruby object
first_record = body_json.first
first_record_object = OpenStruct.new(first_record)
first_record_object.id
POST/create
require 'faraday'
require 'json'
conn = Faraday.new(url: 'http://localhost:3000')
post_data = { post: { title: 'Example Title', body: 'Example Body', published: true, published_at: '2023-04-12T12:34:56Z' } }
response = conn.post('/posts.json') do |req|
req.headers['Content-Type'] = 'application/json'
req.body = JSON.generate(post_data)
end
puts response.body
PATCH/update
require 'faraday'
require 'json'
conn = Faraday.new(url: 'http://localhost:3000')
post_data = { post: { title: 'Updated Title' } }
response = conn.patch('/posts/1.json') do |req|
req.headers['Content-Type'] = 'application/json'
req.body = JSON.generate(post_data)
end
puts response.body
DELETE/destroy
require 'faraday'
conn = Faraday.new(url: 'http://localhost:3000')
response = conn.delete('/posts/1.json')
puts response.body
I usually keep Faraday calls in app/services/* and invoke them from there.
That’s it! Now you can build your own API adapter.
Did you like this article? Did it save you some time?
