 Github Actions. CI/CD basics
Github Actions. CI/CD basics
From my experience, here are some best practices when working on git with a team:
- Disable pushing directly to
mainbranch; - All changes should come via Pull Request (PR);
- A PR should have at least 1 approval (if more than 1 collaborator);
- Disable merging a PR until checks pass;
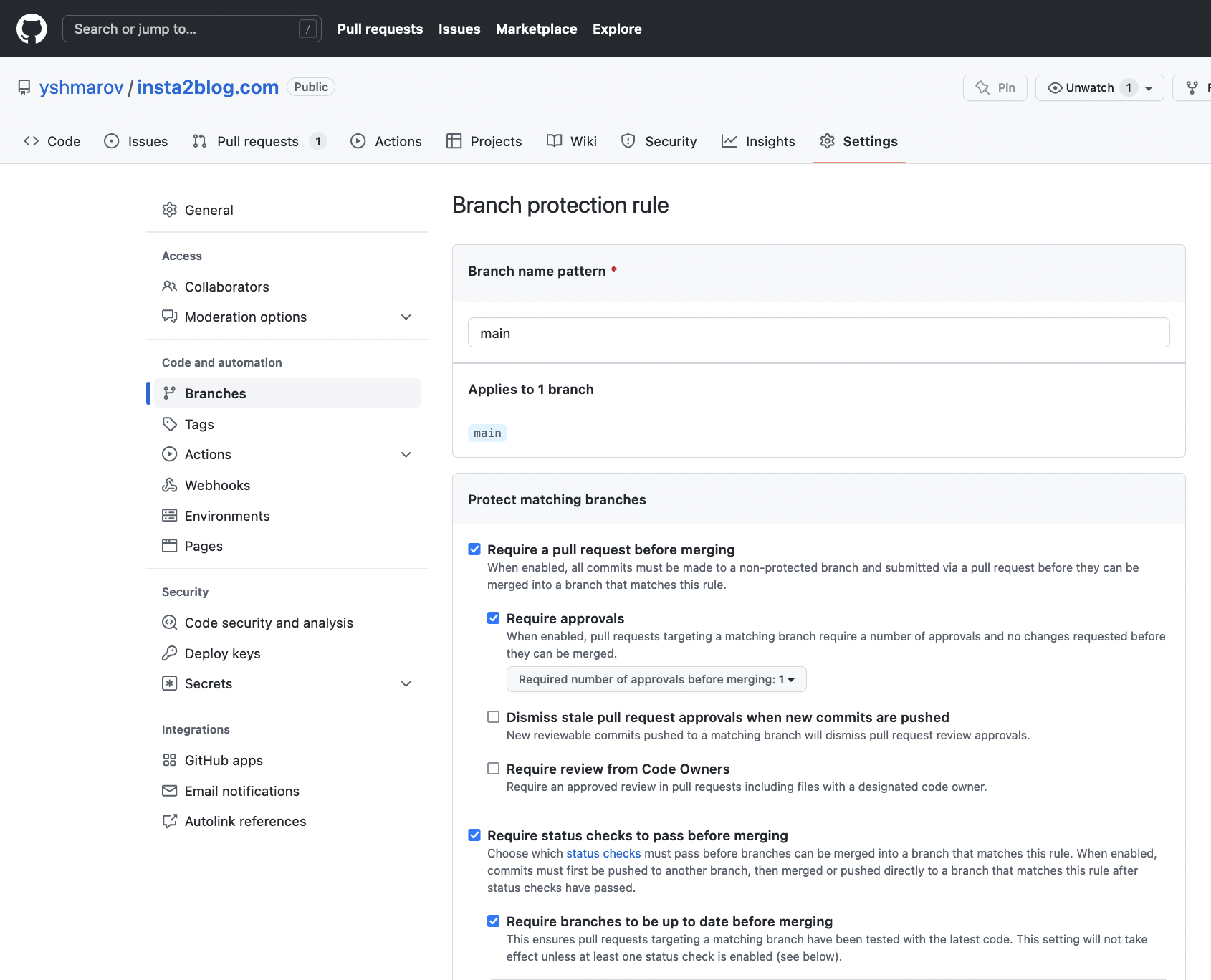
- Also, preferably, “update with rebase” when you can (not “update with merge commit”);
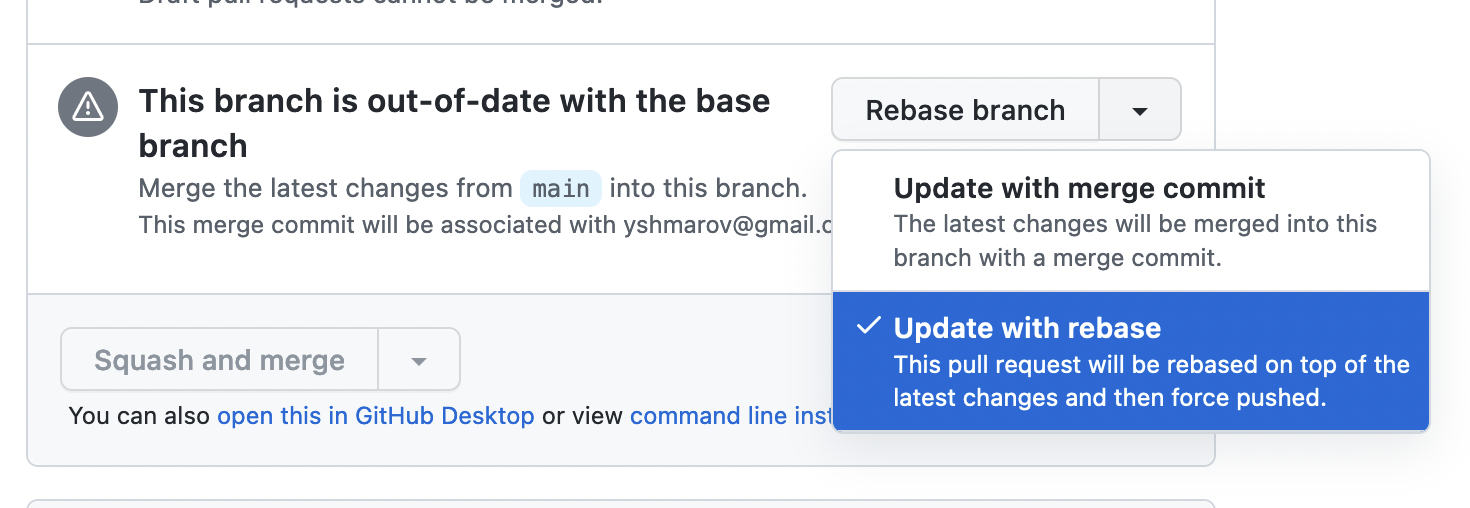
Usually to ensure code quality you would use run tests and linters locally.
Usually code storage solutions like Github/Gitlab allow you to run these tests in a virtual environment.
That way, you and your team can be sure that the tests are successful before merging a PR without having to re-run the tests on their machines.
The Github tool that allows you to run this sort of scripts in a virtual environment is called Github Actions.
To start using Github Actions on a repo, you would need to add a folder like .github/workflows in the root directory of your app.
Next, you could add yml scripts inside the folder. Here’s an example script:
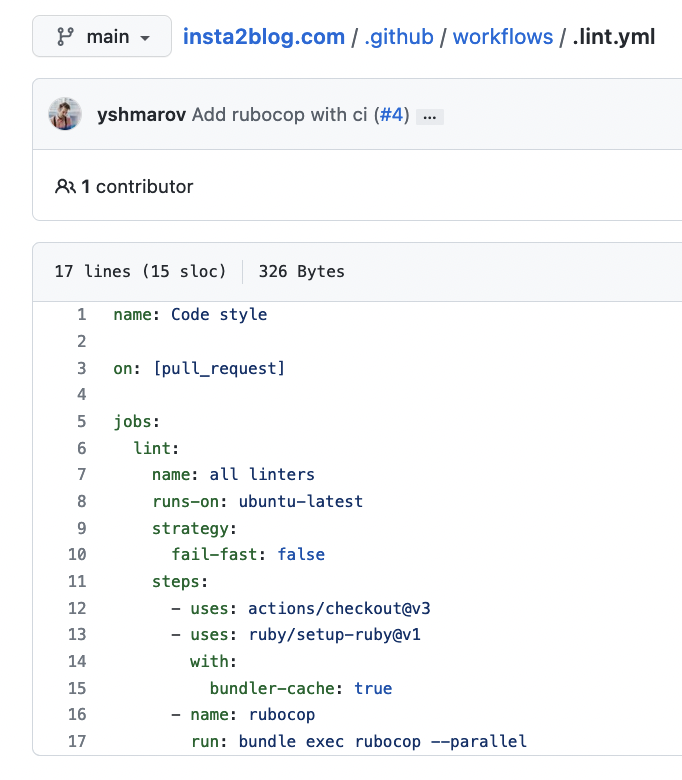
The above script would run rubocop on your app whenever a pull request is created, or commits are pushed to it and provide a success/failure state:
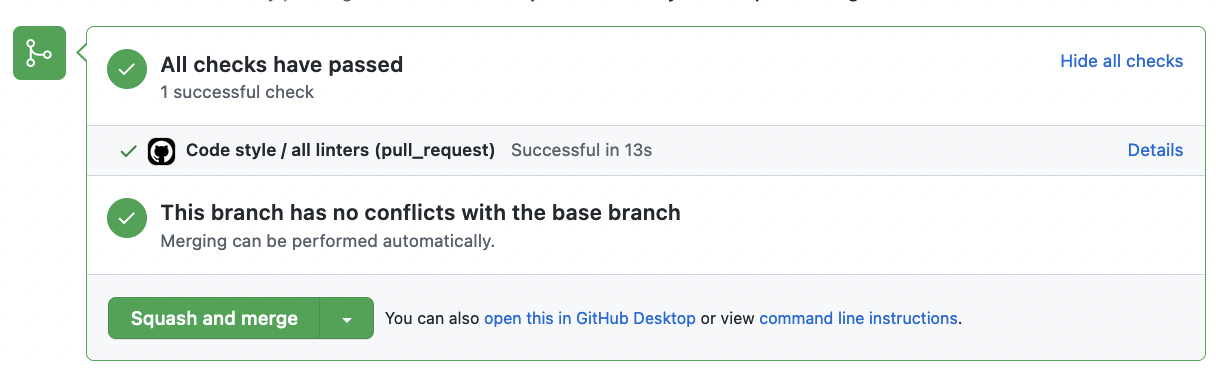
Setting up the CI to run for linters is usally straightforward. You can find the code version of the above script in the article Install and use Rubocop.
The common “Checks” are:
- rspec/minitest tests
- rubocop linting
- erb linting
- javascript linting
- deploying to a PR app
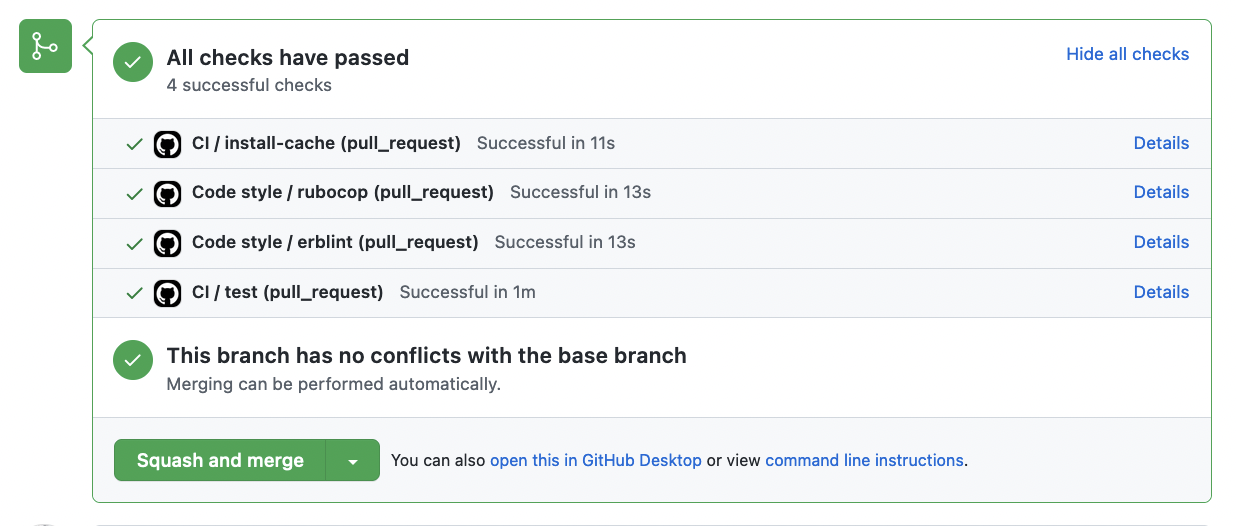
Setting up CI for tests #
This is usually harder, because it requires running the app.
Common “problems” are:
- installing Redis
- installing Postgresql
- adding credentials
Now let’s
- add a basic page to a Rails app
- test the page locally
- finally add a script to test the page with Github Actions
rails g controller static_pages landing_page
<!-- app/views/static_pages/landing_page.html.erb -->
<h1>hello world</h1>
# test/system/static_pages_test.rb
require 'application_system_test_case'
class StaticPagesTest < ApplicationSystemTestCase
test 'visiting the homepage' do
visit static_pages_landing_page_url
assert_text 'hello world'
end
end
To run system tests in CI, you will need to use headless chrome:
# test/application_system_test_case.rb
require 'test_helper'
class ApplicationSystemTestCase < ActionDispatch::SystemTestCase
# driven_by :selenium, using: :chrome, screen_size: [1400, 1400]
driven_by :selenium, using: :headless_chrome, screen_size: [1400, 1400]
end
Run tests:
# bin/rails test
# bin/rails test:all
bin/rails test --fail-fast
Run system tests:
bin/rails test:system
Troubleshoot Github Actions with rails credentials #
Running some tests would require having valid credentials.
Here’s how you can add master.key with a value 34tjk3ngiovv3j409jc34jt90v3q4jt4 to Github Actions using the Github GUI:
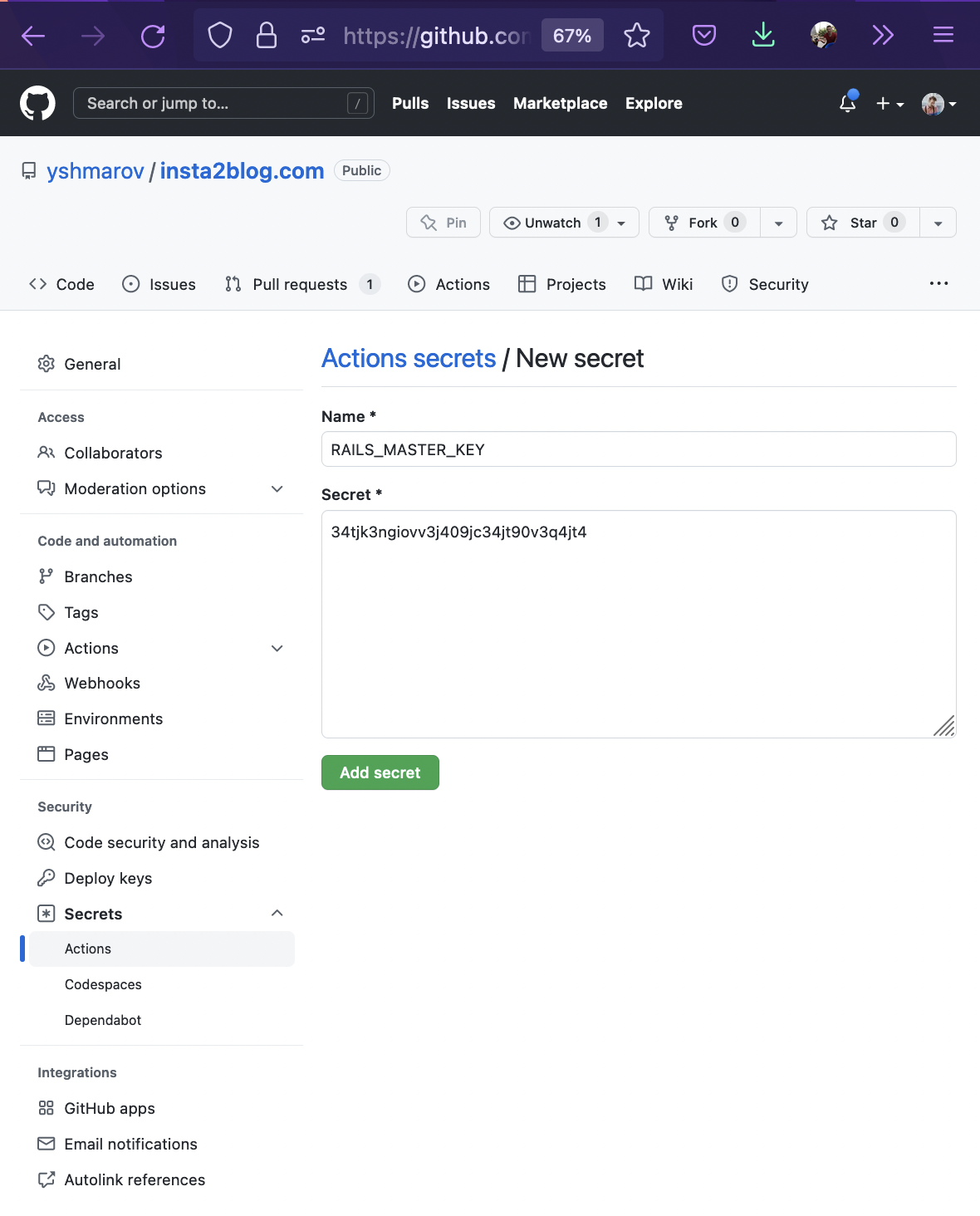
(Name should be RAILS_MASTER_KEY).
It can later be accessed in the CI yaml file as secrets.RAILS_MASTER_KEY ⤵️
Finally, the CI script #
This script works for me to install postgres, redis, run tests, re-run seeds.
# .github/workflows/.tests.yml
name: CI
on:
pull_request:
branches:
- "*"
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
install-cache:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
timeout-minutes: 10
steps:
- name: Checkout Commit
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Install Ruby
uses: ruby/setup-ruby@v1
with:
bundler-cache: true
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
needs: install-cache
timeout-minutes: 10
services:
postgres:
image: postgres
ports: ["5432:5432"]
env:
POSTGRES_USER: postgres
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: password
options: >-
--health-cmd pg_isready
--health-interval 10s
--health-timeout 5s
--health-retries 5
redis:
image: redis
ports:
- "6379:6379"
steps:
- name: Checkout Commit
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Install Ruby
uses: ruby/setup-ruby@v1
with:
bundler-cache: true
- name: Install system dependencies
run: |
sudo apt-get -y update
- name: Run tests
env:
RAILS_ENV: test
DATABASE_URL: postgres://postgres:password@localhost:5432/myapp_test
# RAILS_MASTER_KEY: ${{ secrets.RAILS_MASTER_KEY }}
run: |
bin/rails tailwindcss:build
bin/rails db:create
bin/rails db:schema:load
bin/rails test --fail-fast
bin/rails test:system
- name: Smoke test database seeds
env:
RAILS_ENV: test
DATABASE_URL: postgres://postgres:password@localhost:5432/myapp_test
# RAILS_MASTER_KEY: ${{ secrets.RAILS_MASTER_KEY }}
run: bundle exec rails db:reset
Finally, here are example CI scripts from open source RoR projects:
That’s it!
Did you like this article? Did it save you some time?
